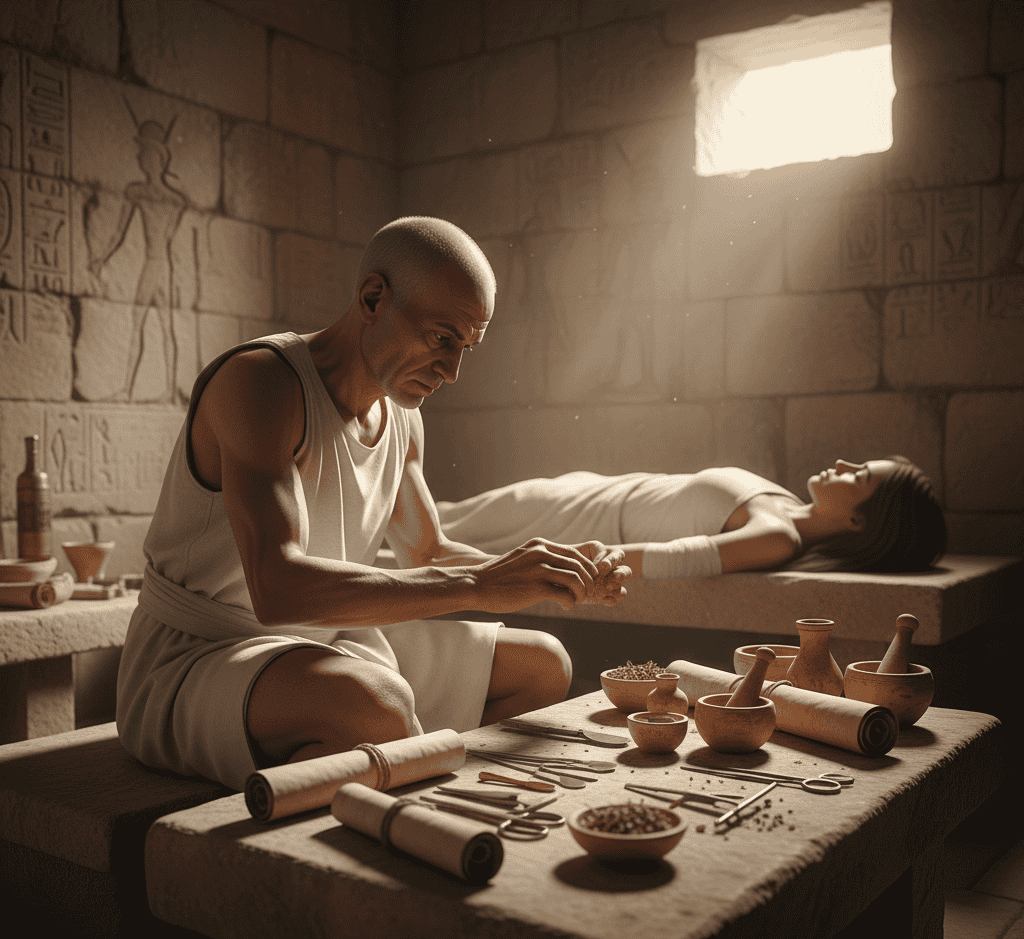
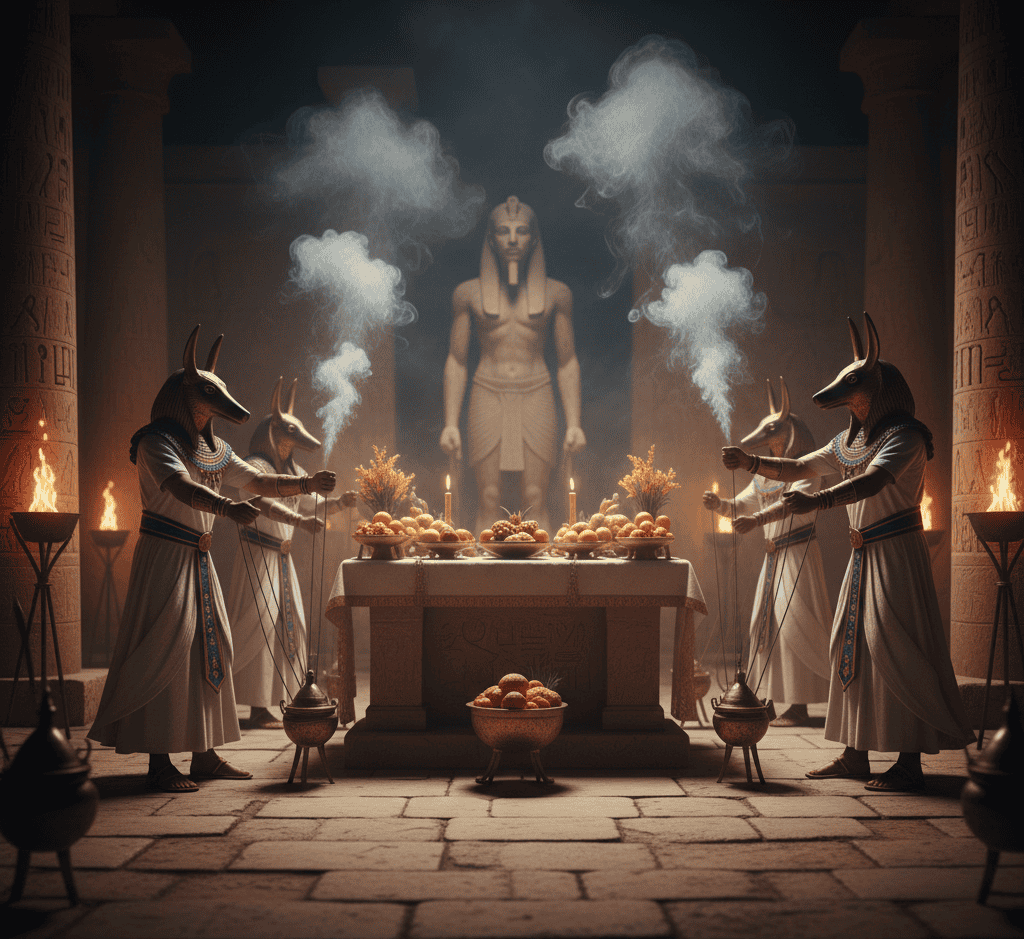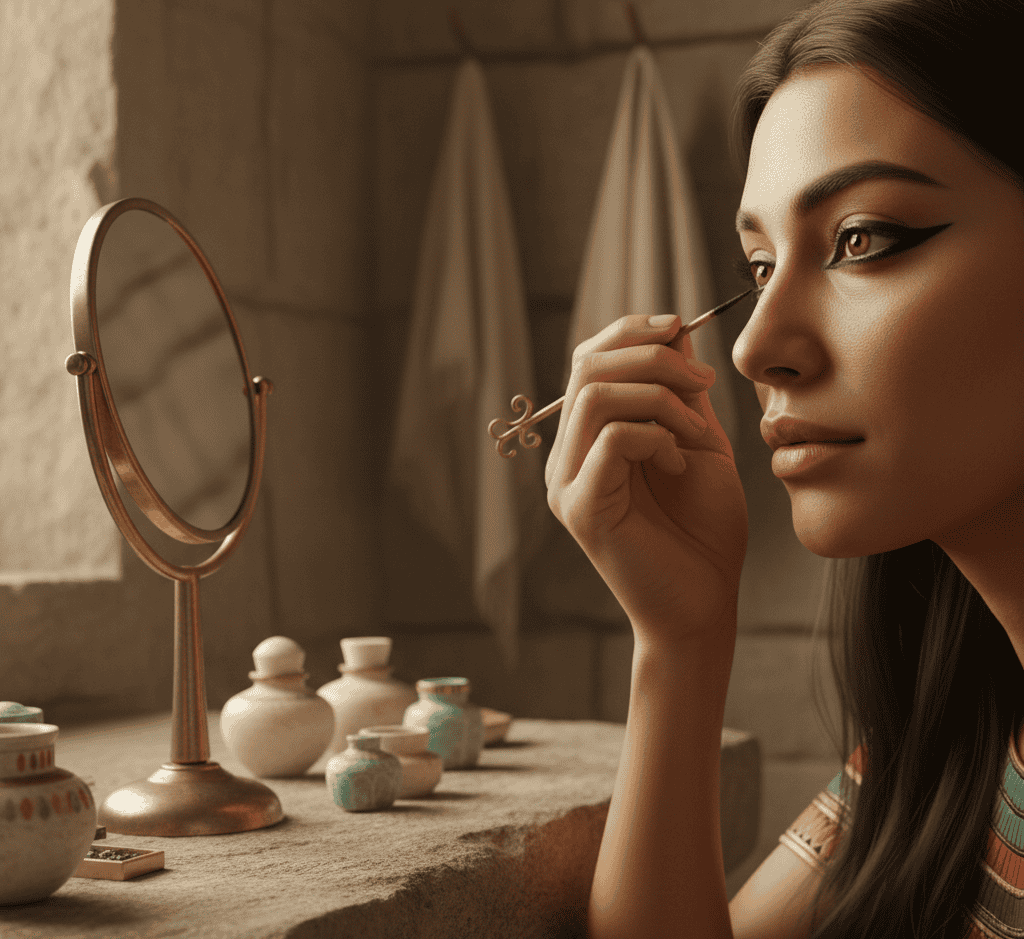Ancient Egypt is one of the most fascinating civilizations in human history, known for its monumental pyramids, pharaohs, and complex religious beliefs.
But beyond the well-known stories, there are lesser-known facts that reveal the depth, mystery, and ingenuity of this culture.
From secret rituals to advanced engineering, Ancient Egypt was far more intricate than commonly imagined.
Archaeologists and historians continue to uncover discoveries that challenge assumptions about daily life, governance, and spirituality in this remarkable society.
These ten shocking facts shed light on the hidden, surprising, and sometimes bizarre aspects of life along the Nile, offering a fresh perspective on this ancient world.
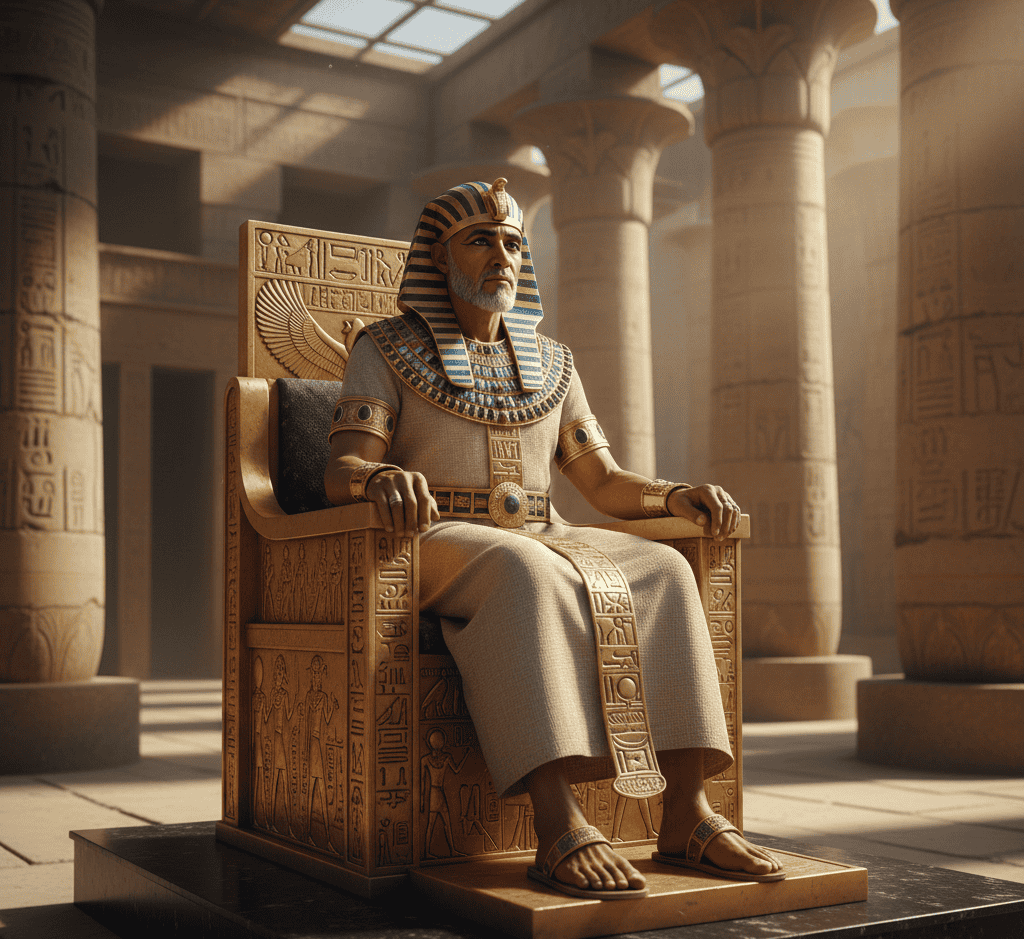
1. Pharaohs Were Considered Living Gods
Egyptian pharaohs were not only political leaders but were also believed to be divine incarnations on Earth.
This status gave them absolute authority, controlling religion, law, and the economy.
People viewed pharaohs as intermediaries between the gods and humanity, responsible for maintaining cosmic order or ma’at.
Their divine status justified immense wealth, monumental construction projects, and strict obedience from citizens.
The concept of living gods shaped Egyptian society, ensuring loyalty, reinforcing social hierarchies, and intertwining governance with spiritual belief in ways rarely seen in other ancient civilizations.
2. The Egyptians Practiced Advanced Medicine
Ancient Egyptians had surprisingly advanced medical knowledge for their time. They performed surgeries, set broken bones, and treated illnesses with herbs, honey, and minerals.
Texts like the Edwin Smith Papyrus describe anatomy, injuries, and treatments in detail, revealing an empirical approach to healthcare.
They also used spells and prayers alongside physical remedies, blending science with spirituality.
This combination demonstrates their holistic understanding of health, showing that medicine in Ancient Egypt was both practical and deeply connected to religious belief, reflecting a sophisticated approach to human well-being.
3. They Believed in a Complex Afterlife
The Egyptian afterlife was highly structured and central to religious life. People believed that proper burial, mummification, and rituals were necessary to ensure survival in the next world.
Tombs were filled with food, treasures, and items for daily use to sustain the deceased.
について Book of the Dead provided guidance through the underworld, detailing tests, gods, and moral expectations.
This belief system shaped architecture, art, and daily life, illustrating the Egyptians’ concern with immortality, spiritual preparation, and the moral implications of one’s actions on life after death.
4. Some Pharaohs Had Foreign Origins
Contrary to popular belief, not all pharaohs were ethnically Egyptian. Throughout history, rulers came from Nubia, Libya, and the Levant.
These foreign dynasties brought unique cultural influences, military tactics, and administrative styles that enriched Egyptian society.
Their reigns demonstrate the civilization’s openness to outsiders and ability to integrate different traditions while maintaining continuity of religion and governance.
This diversity challenges the stereotype of a purely homogenous society and highlights Ancient Egypt as a complex and cosmopolitan civilization with far-reaching connections.
5. Women Could Hold Significant Power
Egyptian women had far more rights and influence than in many contemporary civilizations.
Some became pharaohs, like Hatshepsut, ruling with authority equal to their male counterparts.
Women could own property, inherit land, and participate in legal contracts. Priestesses and queens wielded spiritual and political influence, shaping policy, religious practices, and dynastic succession.
This level of empowerment shows that Ancient Egypt recognized the importance of women in both public and private spheres, challenging assumptions about gender roles in the ancient world.
6. They Used Complex Mathematics for Construction
The construction of pyramids, temples, and monuments required advanced mathematical knowledge.
Egyptians used geometry, measurement, and careful planning to align structures with celestial bodies and achieve remarkable precision.
Techniques included calculating angles, measuring volumes, and designing irrigation systems.
Their mathematical expertise enabled the creation of enduring monuments that still awe modern observers.
These achievements reveal the practical and intellectual sophistication of Ancient Egypt, demonstrating how mathematics, architecture, and religion were deeply intertwined in shaping their monumental landscape.
7. They Practiced Strange and Fascinating Rituals
Many Egyptian rituals appear unusual or shocking to modern observers. Festivals included elaborate ceremonies, symbolic dances, and public processions.
Rituals often involved offerings to gods, animal sacrifices, or symbolic acts of renewal and protection.
Some practices, such as mummification, combined technical skill with mystical rites intended to preserve the soul.
These rituals reflect a worldview in which magic, religion, and daily life were inseparable, illustrating the Egyptians’ belief that their actions directly influenced both mortal and divine realms.
8. Cats Were Sacred and Protected
Cats held a special place in Egyptian society and religion. They were associated with the goddess Bastet and considered protectors of homes, crops, and families.
Harming a cat, even accidentally, was punishable by law. Egyptians valued cats for their ability to control vermin and symbolically connect humans to divine protection.
This reverence for animals highlights the Egyptians’ spiritual connection to the natural world and demonstrates how religion, daily life, and legal systems could intersect in surprising ways.
9. They Practiced Cosmetic Surgery and Beauty Rituals
Egyptians placed great importance on appearance, hygiene, and cosmetics. Both men and women used kohl eyeliner, perfumes, and oils for aesthetic and spiritual reasons.
Some evidence suggests they performed minor surgical procedures, such as tooth extraction, to address health or cosmetic concerns.
Beauty and ritual cleanliness were linked, reflecting beliefs about morality, spiritual purity, and social status.
These practices reveal the Egyptians’ complex understanding of personal care, aesthetics, and symbolism, showing that beauty was both practical and sacred in their culture.
10. Many Secrets of Their Civilization Remain Unsolved
Despite thousands of years of research, many aspects of Ancient Egyptian life remain mysterious.
Hidden chambers, undeciphered texts, and unexplained rituals continue to puzzle archaeologists and historians.
Some tombs, tools, and techniques suggest knowledge lost over time, inspiring speculation about advanced technology, hidden wisdom, or secret religious practices.
These mysteries keep Egypt at the forefront of historical fascination and continue to inspire new discoveries, debates, and theories.
Every excavation uncovers new surprises, showing that the civilization along the Nile is as enigmatic as it is extraordinary.

私は生まれたときから、常に神との強いつながりを感じていた。作家として、また指導者として、私の使命は、人々が最も暗い時代に愛と幸福と内なる強さを見つけるのを助けることである。